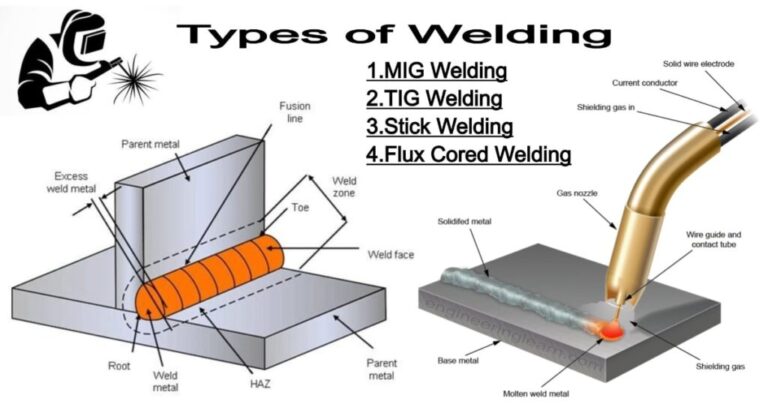
What are the 4 Types of Welding?
Welders aren’t all made equal. Welding is a high-demand trade that you may pursue as a profession. Welding, on the other hand, is a talent that can be used to everyday tasks like as constructing yard art or décor. You can also utilise it to advance in your existing profession, particularly if you work in agriculture or the auto industry. Depending on the type of welding you want to study, the choices are endless.
There are four main types of welding.
- MIG – Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW)
- TIG – Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW)
- Stick – Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW)
- Flux-cored – Flux-cored Arc Welding (FCAW). We dive deeper into each type of welding here.
1. MIG – GAS METAL ARC WELDING (GTAW)
MIG welding is utilised in the automotive sector to repair automobile exhaust systems, as well as in the construction of homes and structures. It is one of the most frequent welding techniques. This is a form of arc welding that employs the use of an electrode, which is a continuous wire. You’ll also employ a shielding gas to prevent against contamination as it passes through the welding gun.
2. TIG – GAS TUNGSTEN ARC WELDING (GTAW)
TIG welding, like MIG welding, employs an electric arc. TIG welding requires the use of a tungsten electrode. Tungsten is one of the most difficult metals to work with. It will not disintegrate or burn away. Welding can be done using a fusion method that uses or does not use a filler metal. An external gas source, such as argon or helium, is also used in TIG.
TIG welding is also used in the aerospace and automotive industries, as well as other industrial areas. Welding waggon frames, fenders, and other critical equipment is also a fantastic form of welding for Iowa since it may be highly valuable for farmers.
3. STICK – SHIELDED METAL ARC WELDING (SMAW)
Do you want to take your welding skills with you? Stick welding has a number of advantages, one of which is its portability. Construction, maintenance, and repair, as well as undersea pipelines and industrial manufacturing, all require stick welding.
You’ll utilise shielded metal art welding, also known as Stick welding, for this form of welding. You’ll utilise a disposable and well-protected electrode, such as a stick. By creating an arc between a covered metal electrode and the base metal workpiece, the stick softens and mixes metals. The stick’s protective layer melts as it melts, shielding the weld region from oxygen and other gases in the air.
4. FLUX-CORED – FLUX-CORED ARC WELDING (FCAW)
Because both use continuous wire and power supplies, flux-cored arc welding is similar to MIG welding. A continuous electrode will be combined with a base metal. The electrode is a flux-filled hollow tube that is injected into the weld pool using the weld cannon. A flux shield protects the welder from the elements when welding outside. This technique of welding is utilised in the machining industry to join thicker metals together.